Navigating the Hydrogen Horizon: An Introduction to Hydrogen Compression
Recently, Hydrogen has been a hot topic so we will help you navigate the hydrogen horizon starting with an introduction to hydrogen compression. In this blog, we will focus on the hydrogen value chain. Several countries are collaborating to establish a new hydrogen economy that aligns with climate goals and is actively embracing national strategies aimed at decarbonization. Subsequently, the hydrogen sector is amid a dynamic transformation, characterized by a flurry of announcements detailing ambitious plans for hydrogen production, importation, distribution, and storage.
At the forefront of this evolution is an urgent need for additional projects to meet these ambitious climate objectives. The surge in hydrogen demand is catalyzing innovations across the entire supply chain, with a spotlight on the pivotal role played by the hydrogen compressor sector.
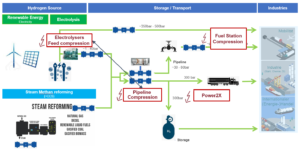
Hydrogen Compressor Application
The choice of a compressor is influenced by application requirements, available space, and overall ownership costs. There are generally four identified roles for compressors in hydrogen applications which we will discuss in more detail.
Injection into the transport grid
Injection into the transport grid:
- It involves boosting hydrogen to approximately 30 to 80 bar, as envisioned for the European Hydrogen Backbone.
- Initially, injection compressors near electrolyzers build up pressure in early-stage national hydrogen distribution networks.
- As networks expand, booster compressors may be needed due to increased pressure losses.
- Compressors are also necessary at injection stations blending hydrogen into existing natural gas streams.
Hydrogen Storage
Here are some key points about hydrogen storage:
- Hydrogen storage is crucial for ensuring a stable supply during periods of lower production.
- Tank storage sites are expected at various scales and locations, both onshore and offshore.
- Salt caverns are being prepared as larger-scale underground hydrogen storage sites, capable of holding larger capacities over extended durations.
- Discharge pressures are anticipated to reach (up to) 200 bara for salt caverns, while storage tanks may operate at even higher discharge pressures.
Fueling Stations
The following are important points to understand fueling stations:
- Compressors at fueling stations present unique challenges due to varying discharge pressures, flow rates, and frequent starts and stops.
- Current discharge pressures range from 350 bar for large vehicles to 700 bar for personal vehicles.
- While hydrogen use in passenger cars may be limited, long-distance heavy-duty transport is a promising application for hydrogen or synthetic fuels.
- Fueling station compressors differ from storage compressors, meeting requirements for high hydrogen purity, relatively small capacity, and intermittent operation.
End-User Demand
With regards to end-user demand:
- Various end-user applications, such as high-temperature heating in industrial processes, feedstock in chemical processes, or power generation, have distinct requirements for capacity, pressures, temperature, and purity of processed hydrogen.
- Tailor-made compression solutions are necessary for individual end users.
- End users near a hydrogen distribution grid with consistently higher pressure than required may not need additional compression.
Image: Adopted from slides by Gunther Machu presented in the “Hydrogen” panel at the 13th International Conference on Compressors and their Systems at City, University of London on 11th September 2023.
Hydrogen Application and Screw Compressors
Within the intricate tapestry of the hydrogen economy, compressors seamlessly assume many pivotal roles, intricately woven into application demands, spatial considerations, and overall ownership costs. In the case of screw compressors, they present significant economic benefits when dealing with situations in the low-pressure range. The most common application will be in the hydrogen production phase or injection into the transport grid.
In our next blog, we will explore the different types of screw compressors, how they can be used in Hydrogen Compression, and some of the challenges they help solve.
Looking Forward
As we navigate the hydrogen horizon, the interplay between compression technologies and diverse applications unveils a landscape ripe with possibilities. Stay tuned for our continued exploration into the challenges, considerations, and transformative potential of screw compressors in the hydrogen realm.
The Future is Hydrogen Compression Blog Series
In this 3 part blog series titled The Future is Hydrogen we explore the growing demand for an eco-friendly hydrogen economy. Hydrogen is becoming a crucial energy carrier with many countries adopting strategies to cut carbon emissions and link different sectors. The hydrogen compressor sector is going to play a pivotal role in this journey so join us as we explore the what, why, and hows of Hydrogen compression.
To stay up to date with PDM Analysis, follow us on LinkedIn here and Twitter here.